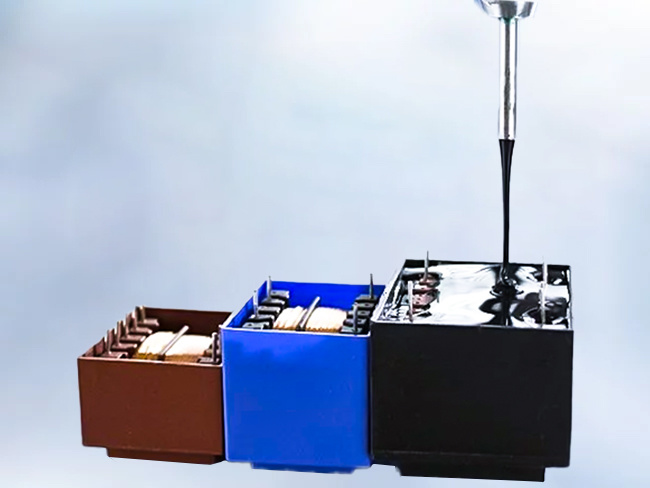
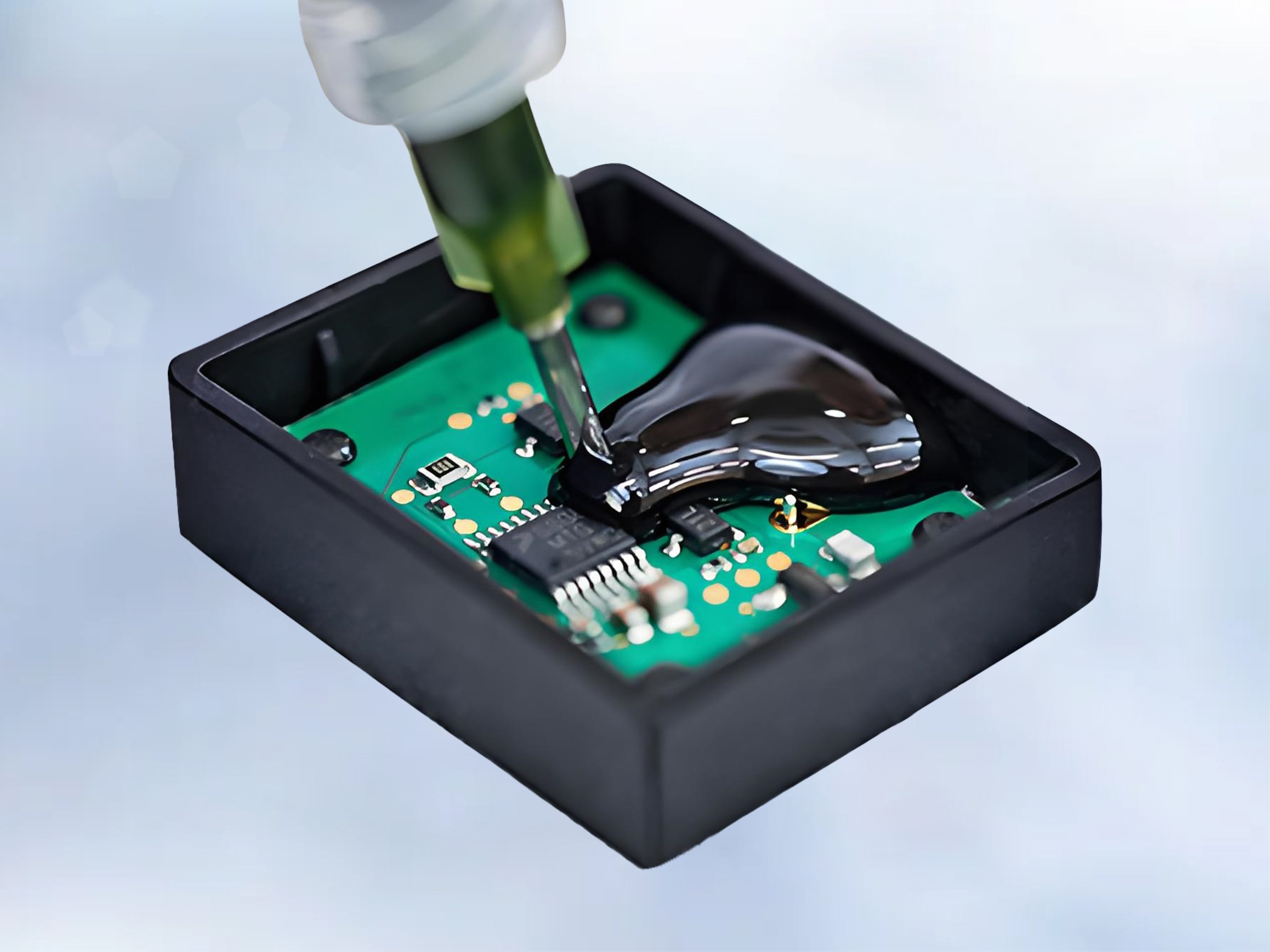
Epoxy resin potting glue
Durability and versatility
Various applications, tailored solutions
Epoxy potting compounds have excellent physical properties such as insulation, compression resistance, moisture and heat resistance, and high bonding strength, which make them widely used in many fields. Whether in motors, electronics, power, medical equipment, the automotive industry, or aerospace, epoxy potting compounds play an important role.
The epoxy potting compounds developed and produced by Hinnel have a rich product and technology reserve in key performance areas such as high temperature resistance, high toughness, low stress, high strength, high adhesion, and crack resistance, capable of meeting various application scenarios.
At the same time, we can adjust various indicators according to customer process requirements. We use advanced equipment to simulate customer production conditions and test the adhesive formulations and applications, which helps determine the suitable products.
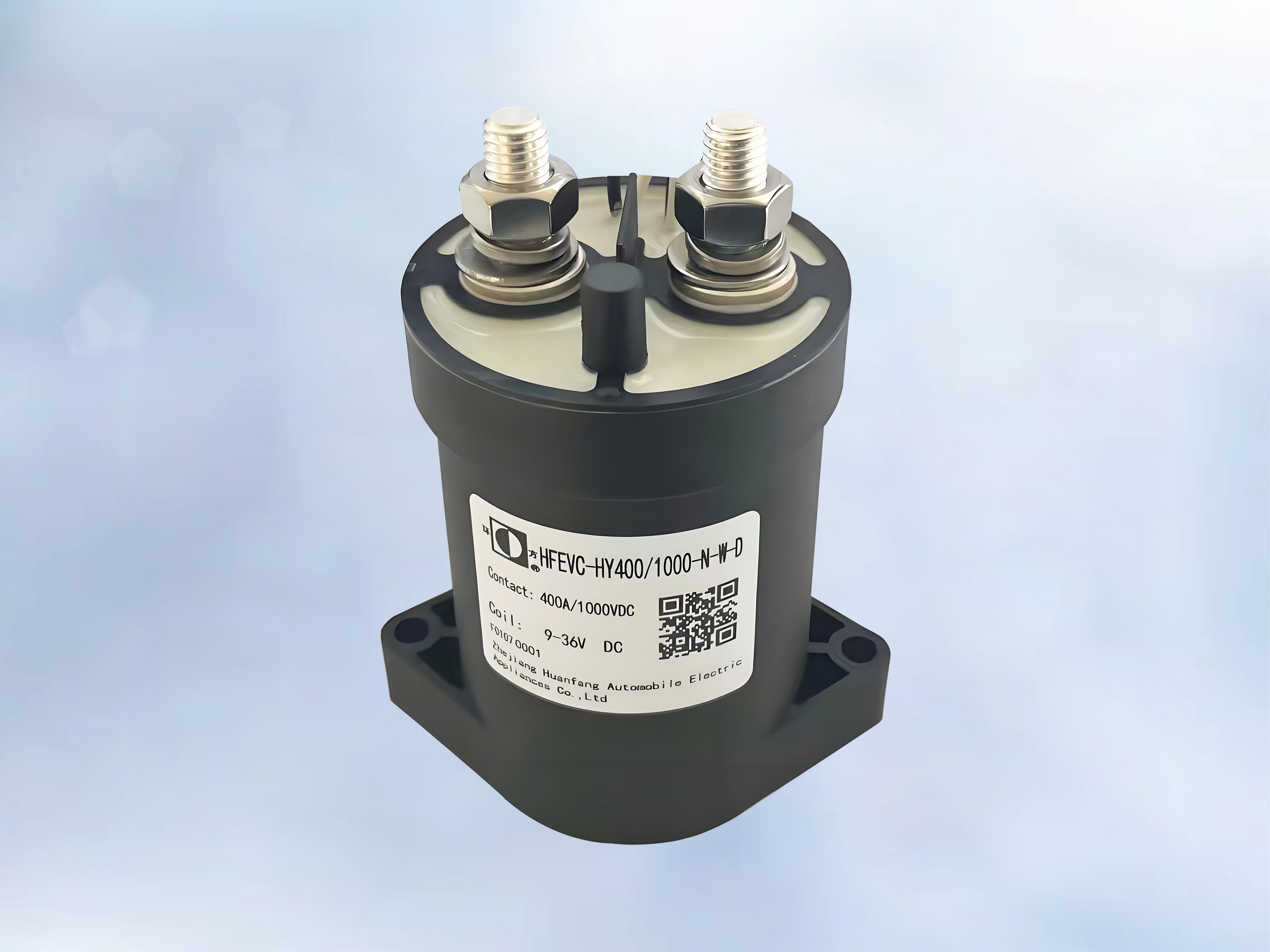
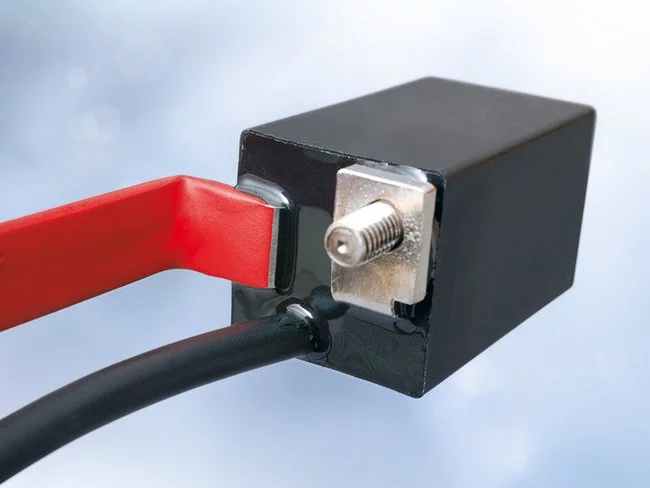
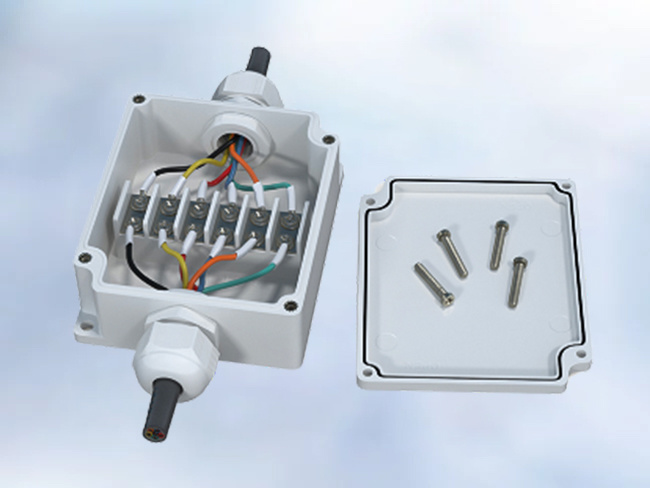
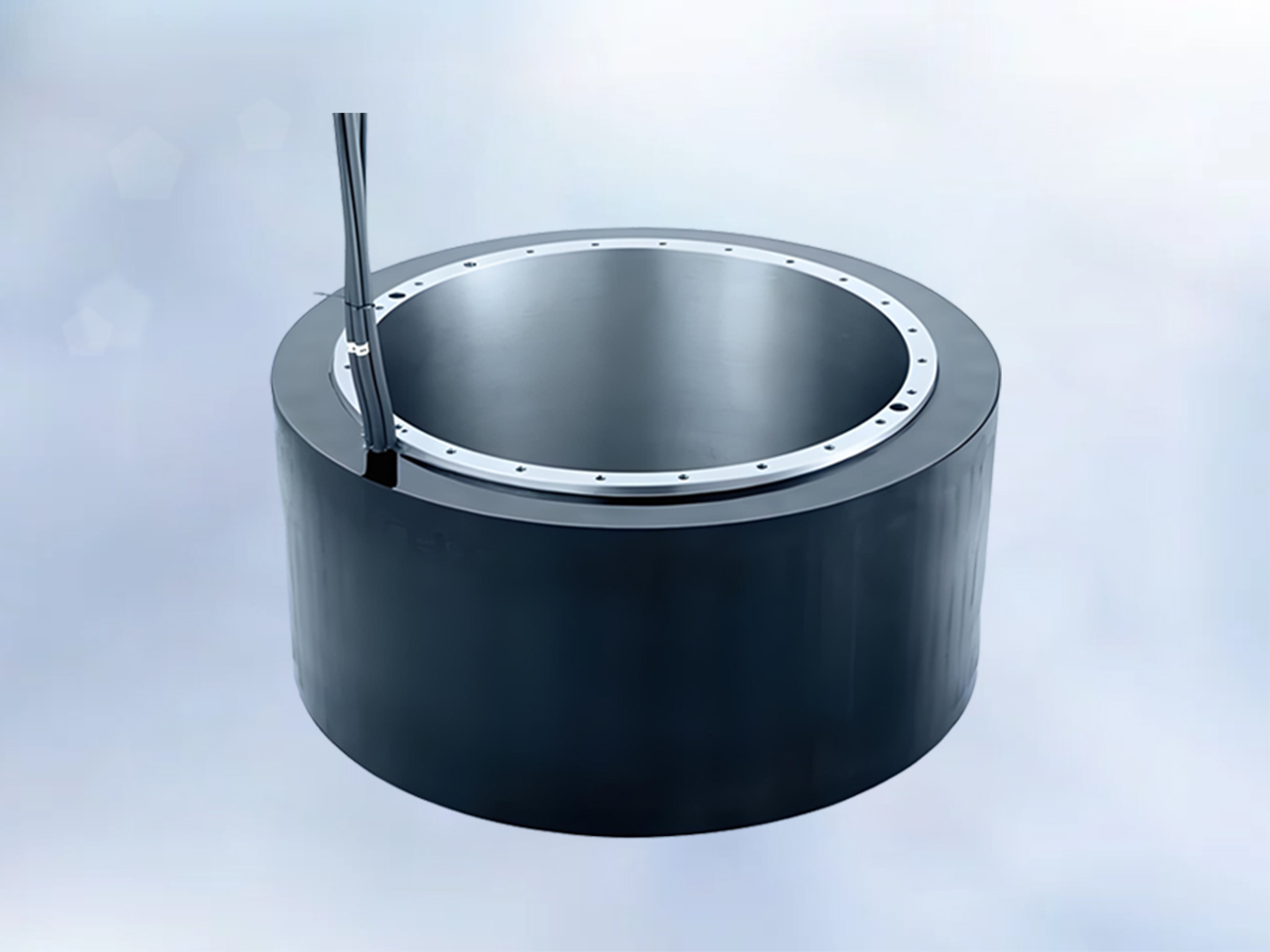
Product applications: potting protection for automotive electronics and sensors; insulation potting for transformers, capacitors, and current transformers; potting for automotive ignition coils and explosion-proof power supplies; bonding and sealing of water treatment membrane components; waterproof potting for smart water meter controllers; potting for industrial linear motors, fan motors, new energy; potting for various motor stators such as automotive drive motors.
Hinnel Product Features
A wide range of products with performance covering high temperature resistance, high toughness, low stress, flexibility, high strength, high thermal conductivity, crack resistance, yellowing resistance, and resistance to thermal shock.
Temperature range covers -50 to 230℃.
Various viscosities.
Fast curing.
Excellent process operability.
Excellent waterproof performance.
From low hardness soft type to high hardness high strength.
Excellent electrical performance.
Flame retardant performance meets UL94V-0 requirements.
Complies with RoHS and REACH environmental certifications.
| Model | Quality Ratio | Mixing Viscosity | Operation Time | Curing Time | Curing Hardness | Thermal Conductivity | Color | Temperature Resistance Range | Flame Retardant Level | Main Characteristics |
| A:B | cps 25℃ | min 25℃ | min 25℃ | Shore | W/m.k | - | ℃ | UL94 | ||
| HNEP9001 | 100:20 | 1200±200 | 50±10 | 25℃×24h or 80℃×2h | 85D | 0.5 | Black | -40~120 | - | General-purpose epoxy potting adhesive, long operation time, bright and smooth surface. |
| HNEP9002 | 100:20 | 800±200 | 30±10 | 25℃×12h or 60℃×1h | 85D | 0.6 | Black | -40~120 | V-0 | Excellent flame retardant performance, 3mm V-0, bright surface after curing, excellent bubble release performance, fast curing speed, can be potting in large volumes without explosion. |
| HNEP6220 | 3:1 | 300±100 | ≥40 | 25℃×24h or 50℃×1h | 80D | 0.2 | Transparent | -40~120 | - | Low viscosity, transparent and yellowing resistant, moderate curing speed, good consistency in high and low temperatures after curing, has toughness, low stress, good adhesion to metal and plastic housings, excellent water resistance and waterproof sealing. |
| HNEP6230 | 3:1 | 300±100 | ≥40 | 25℃×24h or 50℃×1h | 60A | 0.2 | Transparent | -40~120 | - | Low viscosity, transparent and yellowing resistant, moderate curing speed, soft and elastic after curing, good adhesion to metal and plastic housings, excellent waterproof performance. |
| HNEP6225 | 100:15 | 1200±200 | 40±10 | 25℃×24h or 80℃×2h | 80D | 0.5 | Black | -40~150 | V-0 | Low shrinkage during curing, good toughness of the cured product, good electrical performance, excellent mechanical properties and adhesion, resistant to high and low temperatures and thermal shock. |
| HNEP6225D | 100:8 | 2000 (40℃) | 40±10 | 80℃×2~4h | >85D | >0.8 | Black | -40~230 | V-0 | Amine-based, specially developed for applications in motor stators, transformer coils, and devices requiring high hardness, high thermal conductivity, and low thermal expansion coefficient. This epoxy system has high-temperature stability and excellent electrical insulation. |
| HNEP9220 | 100:25 | 3000±1000 | 70±15 | 25℃×24h or 80℃×4h | 90±5 | 0.5 | Black | -40~230 | V-0 | Amine-based, ultra-high temperature resistant epoxy potting adhesive, long operation time, can cure at room temperature or with heat, specially designed for potting products that require high-temperature resistance. |
| HNEP6300 | 100:100 | 12000±2000 | >3h | 100℃×2h+120℃×2h | 85D | 0.8 | Black | -40~150 | V-0 | High TG, flame retardant, thermally conductive, heat resistant, crack resistant, good adhesion to metal and plastic, very low shrinkage rate, resistant to dual 85% >1000h, resistant to -40~125℃ thermal cycling >200, and high-temperature storage tests, the gel does not crack or delaminate. |
| HNEP6310 | 100:30 | 1500±500 | 6~8h | 80℃×2h+120℃×2h or 90℃×4h | 85D | 0.6 | Black | -40~160 | V-0 | Low viscosity, good permeability, temperature resistant, thermal shock resistant potting adhesive, suitable for potting small temperature-resistant and crack-resistant components. |
| HNEP6320 | 100:100 | 1900 (60℃) | >3h (60℃) | 110℃×2h+120℃×2h+ 150℃×2h+180℃×2h+210℃×2h | 95 | 1.9 | Gray | TG>200 | V-0 | Ultra-temperature resistant, low viscosity epoxy potting adhesive, suitable for potting motor stators, transformer coils, and other devices with small diameter compact windings, excellent high-temperature stability and electrical insulation, resistant to thermal shock. Resistant to -45~200℃ thermal cycling. |
Our products are more than that · · · ·
Contact us: get more product information/apply for samples now/work with you to develop solutions tailored to your requirements and processes.
Usage (Ammonia based low viscosity filler system)
Mixing - Before mixing and dispensing, check whether the fillers in the resin have precipitated. If there is precipitation, it must be stirred evenly first. As needed, the resin can be preheated to 40-50 ° C to facilitate mixing. Use manual or automatic equipment to evenly mix the A/B components in proportion (weight ratio), making sure to stir evenly. For large-scale production, automatic measuring/mixing/gluing equipment can be used.
Pouring - Can be done manually or automatically with mixing devices, resin heating devices, and vacuum equipment. Place the pouring port of the component to be sealed horizontally upwards, pour in the sealing glue within the operable time, and self level.
Curing - Cure according to the curing temperature specified in the product technical parameters. If the temperature is low, the curing time should be extended as appropriate. For products with large dimensions and a large amount of glue, they should be poured in batches or the curing temperature should be lowered to prevent excessive heat release from affecting product performance.
Cleaning - When using epoxy resin, it is recommended to use disposable containers and utensils. When disposable materials cannot be used, solvent cleaning equipment can be used to remove uncured sealant. Solvent cleaning tools should be thoroughly dried before reuse; Any residual solvent will cause contamination to subsequent operations.
Instructions For Use (Transparent ammonia based system without fillers)
Mixing - Use manual or automatic equipment to evenly mix the A/B components in proportion (weight ratio), and be sure to stir evenly. In situations where gas mixing is sensitive, the stirred adhesive solution needs to be vacuumed at a vacuum degree of -0.09MPa or above for 3-5 minutes. When there is a large amount of colloid, the degassing time should be appropriately extended. Large scale production can use automatic measuring/mixing/gluing equipment.
Pouring - Can be done manually or with automatic sealing equipment equipped with resin heating and vacuum pumping devices. Place the pouring port of the component to be sealed horizontally upwards, pour in the sealing glue within the operable time, and self level.
Curing - Cure according to the curing temperature specified in the product technical parameters. If the amount of glue is small or the temperature is low, the curing time should be extended as appropriate. For products with large dimensions and a large amount of glue, they should be poured in batches or the curing temperature should be lowered to prevent explosion caused by excessive heat release.
Cleaning - When using epoxy resin, it is recommended to use disposable containers and utensils. When disposable materials cannot be used, solvent cleaning equipment can be used to remove uncured sealant. Solvent cleaning tools should be thoroughly dried before reuse; Any residual solvent will cause contamination to subsequent operations.
Instructions For Use (Anhydride based high viscosity filler system)
Mixing - Use manual or automated equipment to evenly mix A/B components in proportion (weight ratio) until the color is uniform. Large scale production can use automatic measuring/mixing/gluing equipment, but attention should be paid to preventing settlement in the conveying pipeline. It is recommended to perform mechanical mixing in a sealed chamber, otherwise air may be sucked into the sealant product during the mixing process. Minimizing bubbles and gaps is essential for achieving optimal electrical and thermal conductivity of the sealant. Therefore, in critical operations, it is recommended to perform vacuum infusion.
Attention: When the temperature is low in winter, component A will become viscous and difficult to use. It is recommended to preheat it to 60 ℃ in the original packaging. Before mixing the resin and curing agent, thoroughly mix component A to prevent precipitation (HNEP 6300 and HNEP6320 series B components also require this operation). Please make sure to mix the materials evenly in the original container every time you use them, especially if they are not used up.
Sealing - Operated manually or using automatic metering/mixing/gluing equipment. In most cases, it is recommended to use vacuum sealing technology. Small products or products with simpler internal structures can be directly injected, while larger products or products with more complex internal structures can be injected 2-3 times.
Curing - Cure according to the curing temperature specified in the product technical parameters; Small products can generally be taken out of the oven immediately after curing and cooled at room temperature. It is generally recommended to cool larger products naturally in the oven after curing, and then take them out of the oven after cooling to room temperature.
Cleaning - When using epoxy resin, it is recommended to use disposable containers and utensils. When disposable materials cannot be used, solvent cleaning equipment can be used to remove uncured sealant. Solvent cleaning tools should be thoroughly dried before reuse; Any residual solvent will cause contamination to subsequent operations.
Attention - The A/B components should be weighed strictly in proportion, and after mixing, they must be stirred evenly to avoid affecting the curing effect. If the A colloid crystallizes or clumps at low temperatures before use, it can be melted in a 70-80 ℃ oven and then stored at room temperature without affecting its various properties. When heating, the container should be in an open state to avoid damage to the container. It is recommended to use it in a well ventilated area. If it accidentally gets on the skin, it should be washed immediately with soapy water. If it accidentally gets on the eyes, it should be rinsed with water for a long time and the eyes should be opened wide. If the stimulation persists, medical treatment is necessary.
Storage and Transportation
This product is non hazardous and should be stored in a sealed manner away from light and heat. The shelf life is six months. Products that have exceeded their shelf life must be tested for normal performance before they can be put into use. Resins that have been stored for a long time, under abnormal conditions, or have exceeded their shelf life may cause sedimentation or clumping of fillers. Therefore, before use, it is necessary to check the condition of the resin and mix it evenly by hand or with a mixer.
Attention: The curing agent is very sensitive to moisture, and after adding the curing agent, the remaining curing agent should be immediately stored in a sealed container.
Warning Message
Before using this product or any product from Shanghai Hinnel, please refer to the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) and the instructions on safe use and handling on the product label. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us at any time.
Common Problems and Countermeasures
Abnormal Appearance
Pattern printing: The surface pattern printing of epoxy sealant refers to the appearance of patches on the surface after the gel solidifies, usually accompanied by color differences. This type of problem is directly related to the sensitivity of the curing agent and moisture. The control measures are the moisture absorption of the curing agent and the moisture level of the adhesive environment. When the curing agent has high moisture absorption and the environmental moisture is also high, the probability of pattern printing after curing is also higher. Therefore, when epoxy sealant shows pattern printing, choose a curing agent with low moisture absorption or reduce moisture.
Wrinkle: Epoxy sealant wrinkling refers to the phenomenon of waves, unevenness, honeycomb, etc. appearing on the surface after the gel is cured. Most of these problems are related to the severity of curing, and the more severe the product reaction, the shorter the effective self leveling time, resulting in wrinkles that cannot be eliminated by leveling. The more epoxy sealant is mixed, the more intense the reaction will be. Therefore, for products with more sealant, multiple sealants can be chosen. In addition, from the perspective of its own performance, wrinkling and curing shrinkage rate are also related to a certain extent. In terms of products, you can contact us to recommend more suitable products.
Needle hole: Epoxy sealant needle hole refers to the needle tip that protrudes densely on the surface after the gel is cured. This type of problem is related to bubbles, and the formation of needle holes is caused by small bubbles not breaking open before the colloid thickens and solidifies during the discharge process. Therefore, to solve the needle hole problem, three aspects need to be Addressed: First, prolonging the curing time, second, improving the defoaming properties of epoxy sealant, and third, vacuum defoaming treatment before use.
Whitening: The phenomenon of whitening is mainly reflected in the appearance of black or transparent epoxy sealant, which is easily visible due to significant color differences. And this phenomenon is more likely to occur in winter because the temperature is low, and some users store at room temperature for a long time, which leads to crystallization of the glue. Generally, short-term low-temperature storage will not result in crystallization. This kind of situation can be solved by heating the precipitated components and stirring them evenly before using them in the glue formulation.
Oil splatter: Surface oil is caused by excessive curing agent, which is relatively light compared to the main agent. After mixing the epoxy potting adhesive AB, agent B (curing agent) will be on the upper layer. Usually, we require customers to pour agent A into agent B when mixing AB adhesive, and then stir evenly to prevent uneven mixing of the curing agent on the upper layer; Under normal circumstances, epoxy sealant is operated based on weight ratio, so customers are required to use an electronic scale for measurement to prevent excessive curing agent. Excessive curing agent cannot undergo chemical reactions, and due to its light density, it remains on the surface.
Pits: The formation of pits is caused by the air in the epoxy sealant breaking open on the surface, and the adhesive cannot self level. Therefore, there are two reasons for the formation of pits: slow defoaming speed and too fast curing speed. Therefore, from the perspective of the product, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the defoaming speed to adjust the curing speed. The second is to minimize the generation of adhesive bubbles and use vacuum defoaming.
Abnormal Performance
Curing: During the curing process of epoxy resin sealant, there may be situations where it does not cure or partially cured parts do not cure. This situation is usually caused by an imbalance in the ratio, which may be due to incorrect ratio or uneven mixing during mixing.
When using it normally, it is necessary to strictly follow the ratio provided by the manufacturer. The electronic scale to be used should be weighed, and attention should be paid to peeling the skin during weighing. When stirring, the edges and bottom of the container should also be stirred until they reach the mark.
Shedding: Epoxy resin sealing adhesive shedding refers to the phenomenon where the adhesive is sealed into the shell and separated from the shell under certain high and low temperature conditions or at room temperature. Shedding will affect the waterproof and sealing performance.
One possible reason for this situation is that the amount of sealant used in a single application is too large, resulting in high heat release and severe shrinkage and peeling after the sealant solidifies. Another possible reason is that the adhesive strength between the sealant and the shell is insufficient, causing expansion and contraction in a cold hot alternating environment and detachment from the shell. To solve this problem, manufacturers need to provide products with strong adhesive strength to the substrate and low expansion coefficient. Please feel free to contact Shanghai Hinnel to recommend more suitable products.
Cracking: Cracking of epoxy resin sealant refers to the situation where the adhesive itself cracks after curing under certain high and low temperature conditions or at room temperature. Cracking has a significant impact on the performance of the sealant product.
There are generally several reasons for this situation. One possibility is that there are large bubbles inside the glue after it solidifies. Under high and low temperature experimental conditions, the bubbles expand and cause the glue to crack. Another possibility is that the glue has a high coefficient of expansion, which generates significant stress in the alternating high and low temperature environment. The stress is released and the glue cracks. In this case, customers need to contact the manufacturer to recommend epoxy resin sealant with low coefficient of expansion and good toughness.
Shanghai Hinnel provides innovative adhesive solutions for bonding, sealing, potting, thermal conductivity, and protection. Our staff work closely with customers to help them increase the value of their products. In the ever-changing market, we constantly innovate, respond quickly, and are committed to providing professional products and technical support to global customers.